Miniature/Low Oil Circuit Breaker
 |
| Miniature Oil Circuit Breaker Photo Credit - ABB Group |
A low oil circuit breaker employs solid materials for insulation purposes and uses a small quantity of oil which just sufficient for arc extinction. Regarding quenching the arc, the oil behaves identically in bulk as well as low oil circuit breaker. By using suitable arc control devices the arc extinction can be further facilitated in an low oil circuit breaker.
Construction
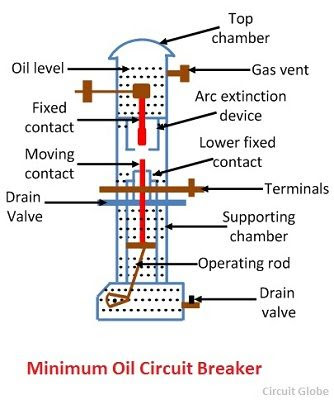 |
| Fig. Miniature/Low oil circuit breaker Photo Credit - Circuit Globe |
- Supporting chamber It is a porcelain chamber mounted on a metal chamber. It is filled with oil which is physically separated from the oil in the circuit breaking chamber. The oil inside the supporting chamber and annular space formed both the porcelain insulation and bakelised paper is employed for insulation purposes only.
- Circuit breaking chamber It is a porcelain enclosure mounted on the top of the supporting compartment. It is filled with oil and has the following parts:-
- Top Chamber It is metal chamber and is mounted on the circuit breaking chamber. It provides expansion space for the oil in the circuit breaking compartment. The top chamber is also provided with a separator which prevent any loss of oil by centrifugal action caused by circuit breaker operation during fault condition.
- Upper and lower fixed contact.
- Moving contact
- Turbulator
Operation
Under normal operating conditions the moving contact remains engaged with the upper fixed contact. When fault occurs the moving contact is pulled down by tripping springs and an arc is struck. The arc energy vaporizes the oil and produces gases under high pressure. This action contains the oil to pass through a central hole in the moving contact and results in forcing series oil oil through the respective passage of turbulation. The process of turbulation is ordinary one in which the section of arc are successively quenched by the effect of separate streams of oil moving across each section in turns and bearing away in gases.Advantages
- It requires lesser quantity of oil.
- The space required is small.
- There is reduced risk of fire.
Disadvantages
- Due to smaller quantity of oil the degree of carbonisation is increased.
- There is difficulty of removing the gases from contact space in time.





Post a Comment